Consisting of a series of steps, the accounts receivable process refers to the money owed to a business for the purchase and delivery of goods or services. In principle the process may appear simple, however in reality it is fraught with complications and challenges.
Accounts receivable (AR) provides the critical link between making the sale and receiving payment. Think of it as an IOU to your business. For instance, the electricity your company uses is invoiced at the end of the service period. Although you’ve already consumed the electricity, payment is made in arrears.
This blog explores the accounts receivable process and its steps, AR key performance indicators (KPIs), AR challenge, and the benefits of AR automation.
The Accounts Receivable Process Explained
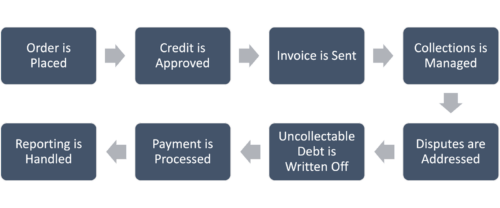
Although AR is an asset on your balance sheet, converting it into cash as quickly as possible is critical to maintaining a positive cash flow. At a high level, this process is accomplished through invoicing and collections, and includes sending the invoice, managing collections, processing payments, matching payments to invoices, and posting the payments. Let’s dig into the details by examining the eight steps in the accounts receivable process.
Step 1: Receive Order
A purchase order (PO) is sent as an expression of the customer’s intent to buy your goods or services. Once the PO is approved, a sales order is created detailing the goods or services being sold to the customer, the quantity and price of the items, and other terms of the sales such as discounts, the delivery date and location, etc.
Step 2: Approve Credit
A critical step to reduce exposure to bad debt, the credit worthiness of the customer is assessed. This process may vary depending on whether the customer is an existing or new client, however the end result will be either credit approval or denial, or the arrangement of alternative payment terms.
Step 3: Send Invoices
Serving as a definitive record of the purchase, the invoice details how much is due and payment due date, as well other considerations such as late payment fees and discounts. Invoices are typically delivered to the customer via email, electronic data interchange (EDI) or regular mail.
Step 4: Manage Collections
Without question, one of the most dreaded AR activities, collections need to be handled both expeditiously and carefully. For example, if payment is past due it is prudent to look internally first to ensure the invoice is error free, it was sent to the customer, and any discounts detailed within the sales order are reflected within the invoice. If the internal review of the invoice checks out, the collections outreach begins. Here are some collections process guidelines that are widely used.
- <7 days past due: Contact the customer with a gentle reminder that payment is due.
- 8 – 14 days past due: Initiate the second contact with the customer.
- 15 – 30 days past due: A dunning letter is sent to the customer stating that payment is 30 days past due: At this stage, late fees may also be applied depending on your internal policies.
- 31 – 45 days past due: Fourth contact with the customer is made and a final letter sent.
- 46 – 60 days past due: Outreach is continued at a predetermined frequency such as weekly.
- 61 – 90 days past due: If the amount owed is significant, senior management, legal counsel, or a collection agency is engaged.
Step 5: Address Disputes
While a few of the reasons for non-payment were touched on in step 4, there are other reasons such as human error in the payment process, issues with the goods or services provided, discrepancies between the proposal and invoice, and communication issues. In the event of an invoice dispute, the customer may pay the portion of the invoice that is not in dispute. Called a short payment, it adds another layer of complexity for your AR team.
Step 6: Write off Uncollectible Debt
Once all outreach efforts have been exhausted, payment may be determined to be uncollectible. Decisions as to whether debt is uncollectible varies by industry, as well as the company’s internal financial policies.
Step 7: Process Payments
To ensure accurate financial records, efficient payment processing is essential. While there’s an assortment of payment methods to choose from, some of the most popular include:
- ACH or EFT
- Wire transfer
- Debit, credit, or virtual card
- Checks
To offer a variety of payments, companies need to have the appropriate tools. For example, to accept online payments the company needs a payment gateway and at least one merchant account, as well as a platform to support eCommerce or self-service payments. To support payments made via checks, the company requires lockboxes (where a bank receives and processes the checks).
Once the payment is made, it is posted to the corresponding invoice(s). The transaction is recorded in the accounts receivable ledger as a credit and deducted from any remaining unpaid receivables.
Step 8: Handle Reporting
During the month end close process, the finance team reviews all recorded transactions and transfers the closing balance of all general ledger accounts into a report (trial balance). This step provides the information needed to create financial statements.
Reviewing your AR status on an ongoing basis enables you to assess accounts receivable process effectiveness, helping the finance team to reach predetermined key performance indicator (KPI) metrics such as days sales outstanding (DSO), collective effectiveness index, and staff productivity.
Track You Accounts Receivable Performance
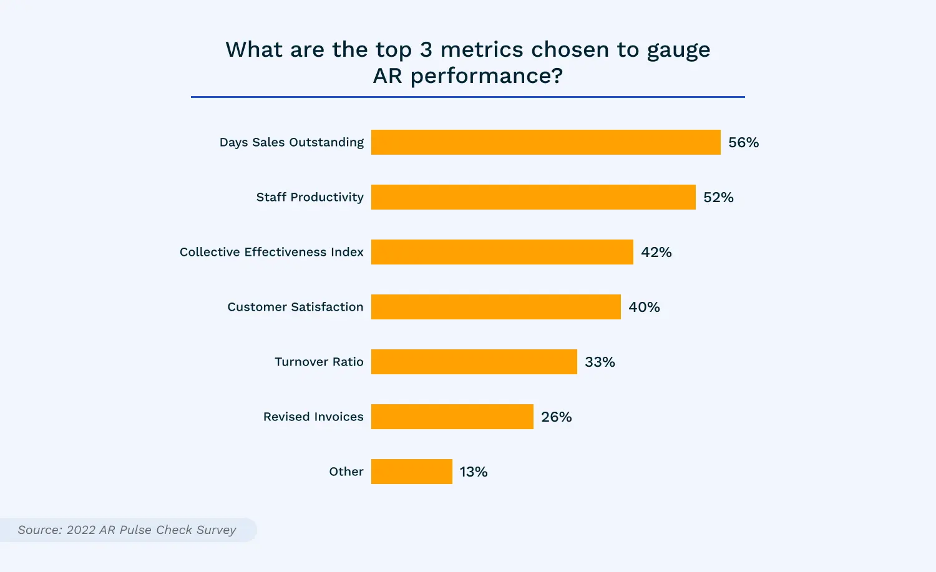
Used to measure performance against goals, finance KPIs directly impact the company’s bottom line. The chart below, sourced by AR Pulse Check Survey, shows the top three KPIs used to measure AR performance – DSO (56%), staff productivity (52%), and collective effectiveness index (42%).
Other KPIs used include reduction in bad debt, a reduction in the percentage of open accounts receivable, accurate cash reconciliation, automation/scalability, and customer satisfaction.
Common Accounts Receivable Challenges
Handling the accounts receivable process manually is riddled with challenges, especially as the company grows and the number of invoices created increases. Let’s look at the top AR challenges from a manual versus automated perspective.
Function | Manual AR | Automated AR |
Invoice Creation | Prone to errors and creation and delivery delays. | Errors are significantly reduced and invoices are created and sent in a timely manner. |
Collections | Ad-hoc collections processes, resulting in invoice backlogs. | Automated dunning and past-due tracking. |
Payment Processing | Prone to errors, as well as processing and cash flow delays. May result in non-compliance to PCI standards. | Bridges gaps in the process via system integration and ensures PCI compliance. |
Financial Record-Keeping | Is tedious and time consuming, prone to errors, lacks the ability to handle complex transactions, and results in report creation delays. | Typically cloud-based, automation provides for real-time record keeping, improves productivity, ensures data accuracy, and allows for complex transactions. |
Cash Reconciliation | Not only inefficient, it is also error-prone, produces inaccuracies resulting from guesswork, and often results in discrepancies between the company’s books and transactional records. | Improves data accuracy to ensure that totals match the balance sheet, cashflow, capital, and income statements, providing for better data-driven decision making. |
Scalability | Difficult, if not impossible, to scale without increasing staff. | Scales easily with minimal manual intervention and effort. |
Error Handling | Higher error rates and lower error resolution rates. | Automatically detects errors, lowering error rates. |
Compliance and Security | Increased non-compliance risks, little to no customer data security. | Provides for enterprise-grade security that follows the PCI security standard and DKIM protocol for sending emails, ensures revenue recognition aligns with ASC 606 and IFRS 15, provides for application-level encryption to keep customer data secure, and provides role-based permissions to ensure control of confidential customer data. |
Reporting and Insights | Basic reporting that is typically manually generated. | Provides real-time reporting, customizable dashboards, and advanced analytics for intelligent insights. |
Customer Experience | Interactions typically happen via email, increasing the chance of the thread becoming buried in the customer’s inbox. Additionally, customer self-service options are limited. | Provides 24/7 self-service access to real-time information, allowing customers to view usage, download statements, view past payments, pay invoices, and manage payment methods. |
Unless you’re running a small business, handling accounts receivable manually can quickly deteriorate. This could be human errors, compliance violations, security risks, and customer dissatisfaction – all of which are costly to your company. However, by automating accounts receivable processes, its shortcomings are virtually eliminated.
The question then becomes – should I automate the accounts receivable process? Aside from the above manual versus automation chart, here’s some questions you should take into consideration.
- Do you have a high volume of invoices?
- Are your transactions growing in complexity?
- Are AR processing errors on the rise?
- Are you encountering an increase in DSO?
- Are you writing off an increasing amount of bad debt?
- Is your financial team not meeting internal KPIs?
- Is your customer churn rate increasing?
If the answer to even just a few of these questions is yes, now’s the time to see how you can benefit from AR automation.
Best Practices for Managing the Accounts Receivable Process
Successfully navigating the AR process requires more than issuing invoices – it takes proactive planning, process discipline, and strong cross-functional collaboration. To maximize performance and reduce costly delays, finance teams must adopt proven best practices that align both strategy and execution across the business.
These practices form the backbone of strong receivable management and provide a scalable framework to handle growth, volatility, or market shifts with confidence.
6 Best Practices to Implement Now
The first step is to establish clear credit policies. A lack of standardization in credit evaluation often leads to payment issues downstream. Documented credit terms, formalized approval workflows, and periodic credit reviews minimize risk exposure and help businesses protect their bottom line. This foundational element directly influences accounts receivable management by filtering high-risk clients before transactions occur.
Once transactions are underway, efficient accounts receivable invoicing becomes essential. Leveraging automation to generate timely and accurate invoices helps reduce discrepancies and promotes timely payment. Templates, predefined delivery schedules, and integration with your CRM or ERP systems support consistency and speed – critical for fast-paced billing environments.
Customer communication should also be front and center. Implementing structured payment reminders – both pre- and post-due – can reduce late payments. These reminders – which could be via email, SMS, or customer portals – reinforce expectations without damaging relationships. Coupled with a thoughtful escalation strategy, they help recover overdue accounts while maintaining goodwill.
To support recovery efforts, develop consistent payment collection strategies that balance firmness with flexibility. Establishing clear dunning workflows, segmenting accounts by risk level, and applying customer-specific outreach protocols makes collections more manageable and less reactive.
Internally, training is critical. Your accounts receivable workflow should be well understood by all teams that impact it – sales, support, billing, and finance. Training helps reinforce understanding of account receivable process steps, from credit approval to dispute resolution, creating tighter alignment and faster issue resolution.
Finally, performance tracking ties everything together. Regularly reviewing metrics like days sales outstanding (DSO), receivable turnover ratio, and collections efficiency offers a real-time look at what’s working and what’s not. Teams gain actionable insights from AR reports, making it easier to adjust policies, identify collection gaps, and improve customer outcomes.
How AR Automation Supports Compliance and Security
As compliance regulations grow more complex and data security becomes increasingly vital, automation is an indispensable tool in the accounts receivable process. By digitizing core AR functions, businesses reduce manual errors, eliminate redundancy, and bring structure to fragmented workflows.
AR automation begins by enforcing standardized billing practices. It applies consistent logic to AR billing, customer segmentation, credit policies, and invoice reconciliation – supporting adherence to revenue recognition standards like ASC 606 and IFRS 15. Transparency is another key benefit. Automation tools create audit trails that track approvals, disputes, and payments, simplifying internal reviews and regulatory audits.
Security improves through encryption, role-based access, and PCI DSS-compliant payment handling. Reducing manual touchpoints lowers the risk of fraud, data exposure, and unauthorized edits. Automation also streamlines regulatory reporting. Real-time data capture and formatting make it easier to prepare investor disclosures, board updates, and financial reports.
Automating the receivable process flow also enhances consistency and builds trust with stakeholders. By strengthening AR processing controls, businesses increase resilience, scale more easily, and meet compliance demands with confidence.
The Role of AR Analytics and Reporting in Decision-Making
In the age of digital finance, data is central to every strategy. When it comes to the steps in accounts receivable process, analytics and reporting are essential for understanding how your AR functions are performing and where improvements are needed. By transforming raw data into meaningful narratives, businesses can elevate the entire accounts receivable automation strategy from reactive to proactive.
- One immediate benefit is better cash flow forecasting. Visibility into customer payment habits, aging, payment history and transaction data allows finance teams to anticipate more accurately. This drives proactive decisions around investment, staffing, and capital allocation.
- Advanced dashboards uncover bottlenecks and risks in the accounts receivable workflow. For instance, repeated invoice disputes from certain customer segments could indicate communication gaps or policy issues. With detailed reports, AR managers can isolate patterns and deploy targeted improvements before cash flow is impacted.
- Customer segmentation is another place analytics shines. Grouping customers by payment behavior, credit risk, or response to outreach helps companies adjust collection tactics and offer dynamic payment terms. These tailored approaches are more effective than one-size-fits-all models and lead to better results.
- Analytics connect AR to strategic planning. These insights inform broader business decisions – like refining sales incentives, adjusting pricing models, or modifying delivery schedules. AR data then becomes a resource for leadership teams across the business.
To support these initiatives, finance leaders need customizable dashboards that track KPIs like DSO, average dispute resolution time, and open receivables by category. These provide actionable insights from AR reports and empower teams to run monthly retrospectives, set quarterly goals, and fine-tune performance.
Notably, analytics support continuous improvement. As teams review what’s working/where delays occur, they can experiment with new strategies, benchmark progress, and adjust accordingly. Whether optimizing cash application efficiency or evaluating collections success, AR reporting becomes the blueprint for smarter execution.
Streamline and Optimize Accounts Receivable Processes
By automating your accounts receivable processes, you’ll gain the ability to simplify and optimize every aspect of the workflow. With AR automation you’ll minimize manual work, reduce errors, speed cash flow, gain real-time business insights, and improve the customer experience. When a modern approach to accounts receivable is adopted, you’ll be able to automate the accounts receivable entire process from invoicing to revenue management and collections, while empowering your customers to serve themselves.
Designed for today’s organizations, BillingPlatform delivers a comprehensive solution that takes you from product inception through to revenue recognition. Our cloud-based solution spans mediation, rating, invoicing, collections, revenue recognition, A/R subledger, and much more – providing you with everything needed to streamline and optimize 100% of your AR business processes.
Are you ready to swap your manual accounts receivable processes for a modern and scalable approach? Request a demo of BillingPlatform today.